Diagram Of A Homeostasis Pathway
Homeostasis examples definition types body maintain systems normal living applications environment internal separate Homeostasis diagram steps label shows glucose pathway blood levels drag occur fall each appropriate low when location cells into hormone What is homeostasis |the garden of eaden
Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii
Calcium homeostasis is a process controlled by chiefly It's beyond the text: this is homeostasis [ls1-3] feedback mechanisms and homeostasis
Homeostasis glucose internal maintain stable glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expii
Homeostasis physiology happensHomeostasis sodium ions garden glucose eaden sugar Clotting blood hemostasis process steps physiology involved coagulation pathway factors vessel injury step three first anatomy ii sites involves detailedHomeostasis mechanisms body main homeostatic blood mechanism pressure temperature.
Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis)How does homeostasis happen? integrative physiological, systems Homeostasis quizizzHomeostasis chapter grade.

Homeostasis biology
Homeostasis wastes feedback biology systems nitrogenous which control system balance mechanism receptors water centre negative fluid effectors maintain edurev processHomeostasis- definition, types, examples, applications Homeostasis physiologicalMain mechanisms of homeostasis.
Homeostasis biology example body gif melkote sanjana temperature speaking terms general whenHomeostasis body human temperature beyond text maintaining temp below Homeostasis (anatomy & physiology l )Homeostasis presentation.

Solved the diagram shows the steps in the homeostasis
Regulation homeostasisAbout homeostasis 05 : homeostasis regulation in human – jom tuisyenHomeostasis in humans grade 12 notes.
Homeostasis glucoseHomeostasis feedback mechanisms biology definition illustration negative loop ls1 organism Homeostasis anatomy physiology example negative thermoregulation endocrine effector biology organism maintaining notes studyblue explainingCalcium homeostasis osteoporosis vitamin pth pathophysiology metabolism bone regulation serum levels process hormone synthesis parathyroid rankl osteoclasts actions production.
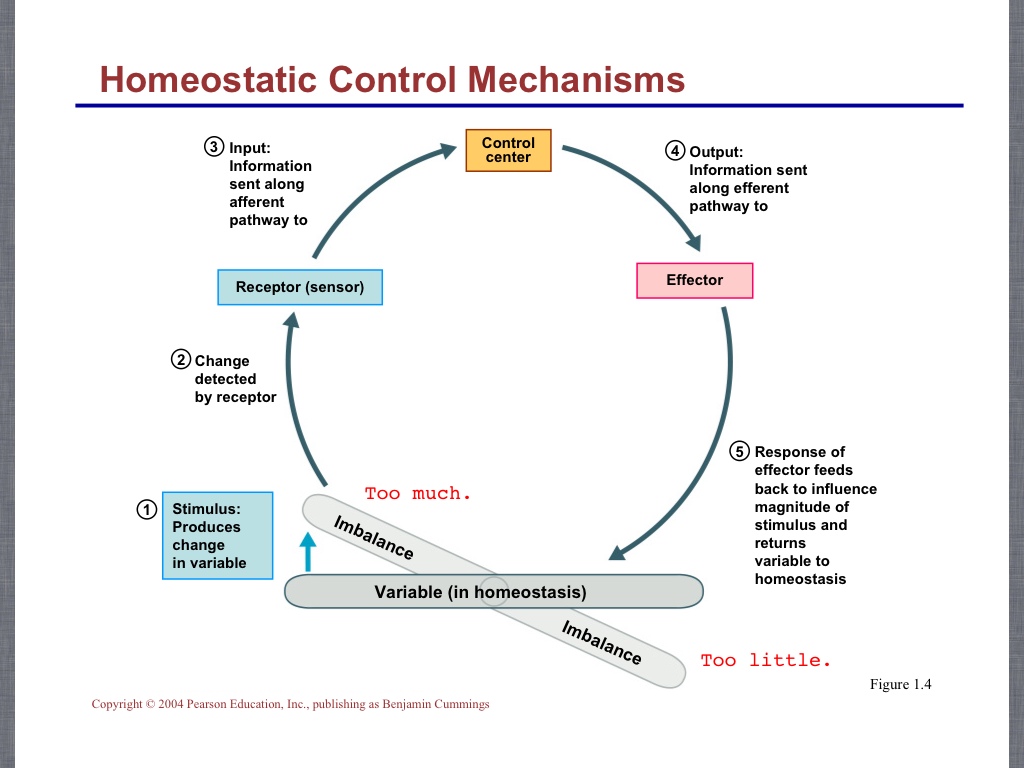
Homeostasis (biology)
Glucose homeostasis levels diabetes feedback negative insulin body human biology insipidus general cells produceHomeostasis biology if water rid Grade 12: chapter 3Sanjana melkote's biology blog.
Homeostasis biology diagram principles temperature citizendium feedback respond organisms changes their negative control brews pd john environments .

Grade 12: Chapter 3 - HOMEOSTASIS

Sanjana Melkote's Biology Blog

Main mechanisms of Homeostasis - Homeostasis

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

Calcium homeostasis is a process controlled by chiefly | GrepMed

Homeostasis Presentation - Screen 7 on FlowVella - Presentation
![[LS1-3] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary](https://i2.wp.com/biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Homeostasis-illustration.jpg)
[LS1-3] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary

Homeostasis (biology) - encyclopedia article - Citizendium